Last Updated on September 6, 2022
Surveying in civil engineering and construction is critical to the completion of many construction projects, including residential and industrial structures as well as infrastructure. It provides project managers and engineers with the geological details they need to construct a structure that can handle the local landscape and helps in the planning of their project.
What is surveying in construction?
Surveying in construction and civil engineering is the collection of different data about the land in the form of civil engineering. Measurements of horizontal and vertical lengths between points, as well as details of the exact characteristics of the land formation and soil, are typical of surveying.

In civil engineering, surveying is also used to determine the three-dimensional relationships between various locations. Engineers use details such as distances and angles between points and lines to decide how to draw plans for public buildings, houses, highways, bridges, and other types of construction and infrastructure projects. To learn all sub disciplines of civil engineering which is related to surveying and geotechnical engineering, check here.
What are Primary Types of Surveying in Civil Engineering?
1. Geodetic Surveying
A geodetic survey takes the earth’s shape, size and curvature into consideration when calculating the exact location of fixed points on earth’s surface. When the areas or distances involved are so far that the required accuracy and precision results cannot be calculated by plane surveying, geodetic surveying techniques are used. Today, geodetic measurements are performed by orbiting satellites that are placed 12,500 miles above the earth’s surface.
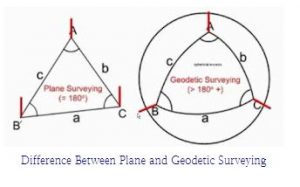
2. Plane Surveying
In order to calculate the topography and composition of a given area of land, a common technique known as “plane surveying” assumes that the area is a flat plane. Because the Earth is not flat, this application of surveying in civil engineering works best for small lands. Because a plane does not account for the earth’s natural curvature, a plane survey carried out over a large area of land is likely to be inaccurate.
What are Methods of Surveying in Civil Engineering?
1. Topographic or Detail Surveys

The aim of a topographic survey is to collect survey data on the land’s natural and man-made features, as well as its elevations. This data is then used to create maps. Typically, the task includes the following:
- Collecting enough horizontal and elevation data from land points to provide enough data for plotting when the map is finished. For example, when surveying for the purpose of improving a taxi rank, the elements to be located include existing side walks, curbs, trees, an island, and so on. For instance, for a road junction, elements such as kerbs, roadmarking (white/yellowlines), and islands will be built.
- Setting up horizontal and vertical controls that will be survey reference points. Leveling is the most accurate way of determining vertical control.
- Calculating elevations, angles and distances.
- The location and shape of natural and man-made features that might be necessary for the survey.
2. As-Built Survey
This type of survey is performed during or directly after a construction project for record keeping, completion analysis, and payment. An as-built survey indicates the location or position of features that have been built and are requiring completion evaluation. Typically, results of as-built surveys are compared to design details. They demonstrate the difference between designed details and constructed details.

The work scope always changes as a development project and its construction progress. Items are moved, added, or removed from the original design. Changes must be recorded in order to demonstrate what was actually built, in addition to being implemented in the field. As a result, the owner typically needs a final record that shows any modifications, or more importantly, any change that modifies the tangible portions of the finished work. This initiative results is what are known as as-built drawings. If we continue to build on top of old projects, land ownership changes, or for public works, these as-built documents become more valuable.
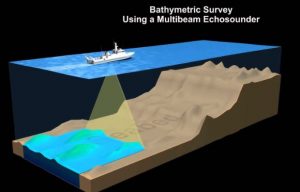
3. Hydrographic Survey
The survey of physical features that are present underwater is known as hydrographic surveying or bathymetric surveying. Measurements of all submerged elements that influence marine activities such as dredging, offshore drilling and marine construction is calculated with the help of hydrographic surveying. The majority of hydrographic surveying is done for official purposes. For shallow water, it is mostly done via sensors, sounding equipment, or electronic sensor systems. In order to prepare the nautical charts, information from hydrographic surveys is necessary.
4. Engineering Survey
Engineering surveying is locating natural and artificial features on or below the Earth’s surface and using these elements in the planning, design and construction works. Any engineering project must have it. The project faces the risk of costly, time-consuming mistakes or even catastrophic failure without an accurate understanding of the size, nature and shape of the site.
5. Archeological Survey
A specific form of land surveying known as “archeological surveying” is done to explain how an archaeological site interacts with the surrounding area or to record the discoveries made there. This survey typically uses GPS, GIS, aerial photography and other surveying methods and is usually requested by archaeologists or government organizations. These surveys are often conducted remotely to prevent disturbing the archaeological site.
6. Aerial Survey
Aerial survey is a method of gathering geographic data with the aid of flying vehicles. Information can be gathered using a variety of technologies, including laser, radar, aerial photography and remote sensing images captured in the gamma, infrared or ultraviolet spectrum of the electromagnetic spectrum. The information gathered needs to be georeferenced in order for it to be useful. Information is typically georeferenced using GNSS and methods similar to those used for dynamic land surveying.

What are Surveying Equipments used in Civil Engineering?
1. Total Station
It’s important to provide a way to verify the accuracy of measuring and surveying data in the construction, engineering, and many other industries. Total stations, thankfully, offer a solution. These light and portable equipment assist you in collecting data you need to ensure quality design and project completion on time.

Total station is a type of optical instrument that is widely used in construction, surveying, and civil engineering. It may measure horizontal angles, vertical angles, and distance by observing the slope between itself and a given location. In one precise and stable instrument, a high-quality total station combines surveying, imaging, and high-speed 3D scanning. It combines the most modern field technology with advanced technological functionality to build a device that is dependable and trustworthy in challenging field scenarios while generating accurate analysis and engineering results.
With today’s advancements in technology, total stations can give very precise location spotting for points on a constructions site, even indoors. Once you know where you are in relation to the corners of a CAD blueprint. You can mark where electric, water and HVAC lines will need to be implemented. This helps take the guess work away and helps the speed of those trades to complete the task at hand. With just a swivel of the machine on a stand from a central point on the outside you can pinpoint the corners of your building and land. If you get to a site that already has been built, the total station can verify the corners and make exact adjustments if points are not exactly where they should be according to the plot maps this way your internal marks will still be where they need to be.
2. Auto-Level
Auto level, also known as a builder’s auto level, a leveling instrument, or an automatic level, is a type of optical instrument used to determine or check points in the same horizontal plane. It is used at surveying in civil engineering with a vertical staff to measure height differences, as well as to transfer, measure, and set heights.

The level instrument is mounted on a tripod and, depending on it’s type, is either approximately or accurately leveled using footscrews (levelling screws). The user looks through the telescope’s eyepiece and an assistant holds a tape measure or graduated staff vertical at the selected location. During site surveys or building renovation, the instrument and staff are used to collect and/or carry elevations (levels). In certain cases, measurement begins with a baseline with defined height calculated by a previous test, or with an arbitrary point with an estimated height.
3. GPS
GPS, which was originally designed for military use, is now widespread. GPS is used in a variety of applications, including smart phones, in-car navigation, and search and rescue devices. However, there is a wide range of surveying equipment and techniques available.

GPS was quickly adapted for surveying because it can explicitly provide a location (Latitude, Longitude, and Height), eliminating the need to calculate angles and distances between intermediate points. Survey control could now be built almost anywhere, all that is needed is a clear view of the sky so that the GPS satellites’ signal could be received clearly.
What is the Importance of Surveying?
Surveying measurements are used in the planning, construction, and maintenance of all civil engineering projects. A detailed analysis of the target area is normally required to decide its exact boundaries and to ensure the safety of any buildings or other facilities built there. Surveyors also seek to ensure proper infrastructure planning and construction, to protect the local natural environment, and to improve the functionality of planned buildings.
- It helps in the development of topographical maps that show both natural and man-made features.
- It helps in the preparation of cadastral maps that indicate the borders of estates, servitudes, and other property rights.
- It helps in the creation of an engineering map that illustrates the information of engineering works such as bridges, railways, reservoirs, and so on.
- It helps to create a contour map to evaluate the steepness or gentleness of slopes.
- It helps in the establishment of horizontal and vertical control point locations during control surveys.
- It helps in building surveys, surveys necessary for the establishment of points, lines, and grades, and staking out engineering work.
What does a surveyor do?
The topographic survey is the most common form of surveying in civil engineering. Topographic (land) surveyors concentrate on the characteristics of the land itself. This might include collecting data on the distances and angles between key points, measuring relative elevations, and determining the condition of the soil (rocky, grassy, etc.).
Topographic surveys can provide information on both natural features (such as hills and rivers) and human-made structures (roads, power lines, etc.). Topographic surveys may also be used to create maps by a property surveyor or land surveyor.
In the fields, land surveyors measure land to decide the boundaries of lands, which helps in determining where houses or roads can be built. Surveyors gather information that is used to build maps. They also help in the resolution of land or property disputes. Surveyors work on a variety of projects, such as land subdivision, detail surveys, setting out, and construction. They are specialists in deciding the size and dimensions of land.
History of Land Surveying
As long as major constructions have been built, surveying has existed. The pyramids of ancient Egypt are proof of their mastery at surveying. However, Ancient Egyptian surveyors also set land boundaries, which were then used for both taxing and determining who owned the property. Surveyors were also regularly reevaluating boundary markers along the Nile River to guarantee that river overflows could be checked and that buildings and construction sites could be maintained secure.

Records from 1400 B.C. show that the Egyptians used surveying knowledge and techniques to divide territories, setting the course for modern land division. Unsurprisingly, taxation is the reason for this work. Since then, Surveyors have forged aheadand remained the pioneers of discovery—both on the land and in the application of technology to change our natural and constructed environments. Our mathematical work is built on the science of geometry, which was created by the Greek surveyors in 120 B.C. They utilized this knowledge together with one of the first survey tools, a diopter, to divide up land.
2000 years later, in 1800 A.D., the science of geodetic and plane surveying was developed, further emphasizing the value of precise boundaries and the locations of important public works like canals, railroads and highways. This was the background to the industrial revolution and the beginning of an even closer relationship between surveyors and engineers in terms of how we record the present to inform the construction of the future.
Surveying in civil engineering has been explained in this article. Hope you enjoyed it!

